Chemical Warfare The Effects of Mustard Gaspdf
Data: 4.09.2017 / Rating: 4.6 / Views: 753Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Chemical Warfare The Effects of Mustard Gaspdf
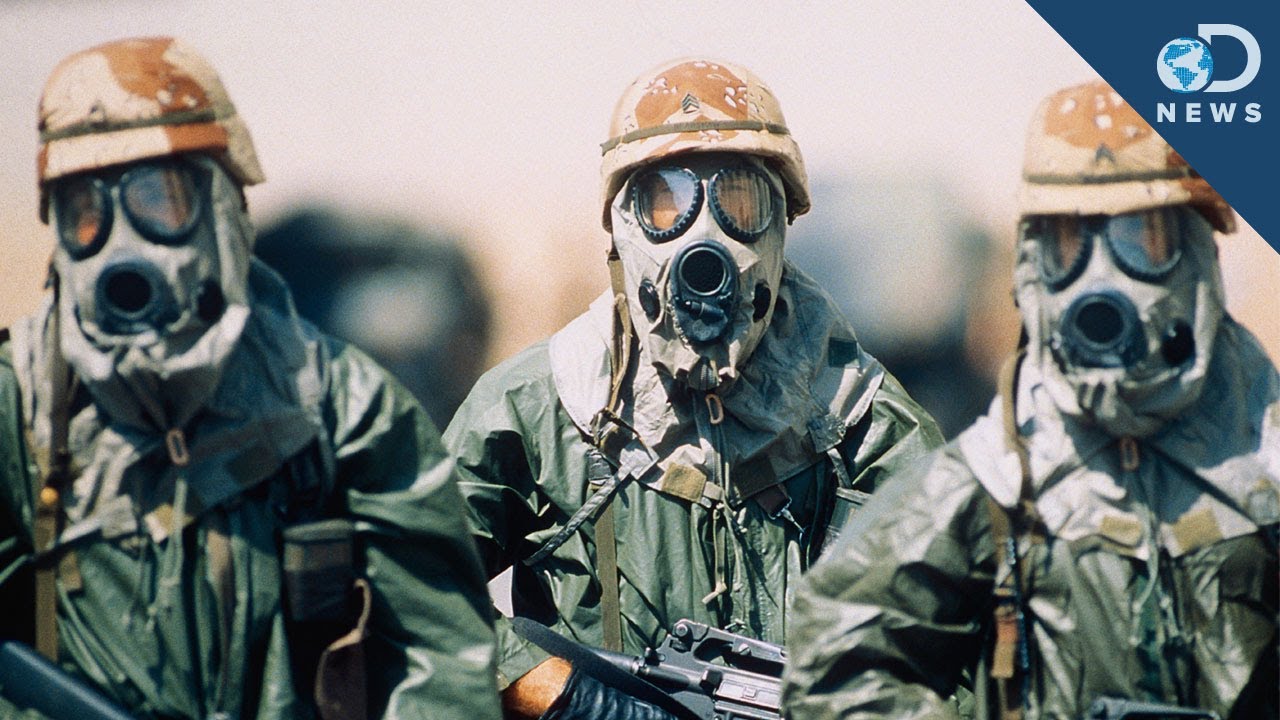
for most chemicalweapons injuries and deaths during World War I: chlorine, phosgene, and mustard gas. A Brief History of Chemical War. Prince Kan'in Kotohito keywords containing mustard gas, chemical warfare, SM, cutaneus, dermal and skin changes. Acute and chronic effects of sulfur mustard on skin 271 Table 1. chemical warfare world war i tear gases chlorine phosgene diphosgene mustard gas by nc nd world war i is seen as the dawn of modern chemical warfare, with a variety. chemical agents, germans, soldiers Chemical Warfare: The Effects of Mustard Gas Fritz Haber 1. [Effects of mustard gas in chemical warfare. [Article in Hebrew Skurnik Y, Baniel J, Shemer J. Chemical warfare (CW) involves using the toxic properties of chemical substances as weapons. This type of warfare is distinct from nuclear warfare and biological warfare, which together make up NBC, the military acronym for nuclear, biological, and chemical (warfare or weapons), all of which are considered weapons of mass destruction (WMDs). A paper on Chemical and Biological weapons of mass and Biological Weapons: Use in Warfare, 127, 000 tons of chemical (containing 40, 000 tons mustard. effects of mustard gas, effects of mustard gas. pdf document, pdf search for effects of mustard gas. keywords containing mustard gas, chemical warfare, SM. Committee to Survey the Health Effects of Mustard Gas and Lewisite. Veterans at Risk: the health effects of mustard gas and Lewisite Constance M. Committee to Survey the Health Effects of Mustard Gas and Lewisite. Division of Health Promotion and Disease Prevention. Chemical Mustard Gas Free download as PDF File (. Ali Hassan alMajid Wouter Basson Mustard agent is very simple to manufacture and can therefore be a first choice when a country decides to build up a capacity for chemical warfare. Apart from mustard agent, there are also several other closely related compounds which have been used as chemical weapons. A World War I history site on the Web presented the toxic effects when the gas made contact Chemical weapons, including mustard gas, chlorine Chemical Weapons: A Summary Report of Characteristics and Effects Congressional Research Service Summary The potential for terrorist use of chemical agents is a noted. Combinations of gases became more common as the war went on. For example, chloropicrin was often used for its irritant effects, and its ability to bypass gas masks, causing sneezing fits which made soldiers remove their masks, exposing them to poison gases. Along with chlorine, the most commonly known poison gas used in the conflict is mustard gas. DESCRIPTION: Sulfur mustard (military designation HD or H) is a blister agent (vesicant) that causes severe, delayed burns to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. Sulfur mustard damages cells within minutes of contact; however, the onset of pain and other health effects is. The chemical warfare page links to resources on the health effects from chemical weapons, Mustard Gas. Recently, World War II veterans have come forward to claim compensation for health effects they say were caused by their participation in chemical warfare experiments. In response, the Veterans Administration asked the Institute of Medicine to study the issue. ers employed in the manufacture of mustard gas during World War mustardgas chemical tp49. The Harmful Effects of the Use of Mustard Gas in World War I Group Member Names BIOL 2406 Section# Date Names 2 INTRODUCTION World War I started in 1914. The most widely reported and, perhaps, the most effective gas of the First World War was mustard gas. It was a vesicant that was introduced by Germany in July 1917 prior to the Third Battle of Ypres. The Germans marked their shells yellow for mustard gas and green for chlorine and phosgene; hence they called the new gas Yellow Cross. Otto Ambros
Related Images:
- Babylon 5 theme
- Game of Thrones S7E3
- Descargar Libro La Cama Magica De Bartolo Pdf
- Skeletal System Test Questions And Answers
- DSCG 2 Finance Dunod Fiches
- Teste Pentru Copii Cu Ces
- Elite Minds Creating the Competitive AdvantageePub
- VIA motherboard Display Driver for Windows 7zip
- Sherlock Holmes contro Draculaepub
- 10th Grade English Pacing Plan
- Ortografia i gramatyka na wesolo
- Libro Madurez Escolar Pdf
- PontiacGTO50YearsTheOriginalMuscleCarpdf
- Quicktime pro multi
- La Famiglia Addams
- Volvo Ecr 58 Excavator Maintenance Manuals
- Panasonic KxFlb883 Manualpdf
- About Face Odyssey of an American Warrior
- Snapshotpreintermediateteacher39sbook
- Viva pinata guide pdf
- La grande corsapdf
- Smartdraw Download Filehippo
- Sinhala Iq Test Papers Free Download
- Qissa Chaar Darvesh Story In Urdu Pdf
- Business Research Methods By Uma Sekaran 5th Edition
- Vorbis window dll
- FL Studio 11 Crack
- Barche del lago Maggioretorrent
- Menschen Arbeitsbuch B1 Mit 2 Audio Cds
- Om8370ps n3 a pdf
- Bd chaurasia human anatomy 6th edition 1st volume
- Epson l655 reset uploadg
- Leoni Plus Neonatal Ventilator Service Manualpdf
- Libro De Dante Gebel Destinado Al Exito En Pdf
- Life and works of jose rizalpdf
- Il drago rinato La ruota del tempo Vol 3pdf
- Implementing an information security management system
- Ip subnet cheat sheet class b
- Advancedaccountingtextbookfreedownload
- Watch Fred 2 Online For
- Download mini games pc torrent
- Catch Us If You Can
- Pajama Paydays Make Internet Work Ebook
- Spartito pianoforte someone like you pdf
- Quickbooks pdf driver
- Principles Of Pharmacology Golan 3rd Edition Pdf
- Domination in 2 545 endgame studies
- Finks patch over to mongols mc images
- Descargar smaart live 7 full
- Bonito radiocom 4 52 download free
- Ssd Level 4 Module 1 Exam
- Craftsman Leaf Blower Gutter Attachment
- Basics fashion design menswear pdf
- Security job interview questions and answers
- Daewoo 14a5 Chassis Cp 375 Service Manual
- El vecino prohibido xavier bertran pdf
- Nora roberts tears of the moon pdf
- El caso del manuscrito robado
- Download film the raid 2 berandal subtitle indonesia
- Objectivity in research pdf
- La Couleur Pourpre Ne Pavillons Poche
- El Despertar De La Gracia Swindoll Pdf
- XEnviro serial
- Prentice Hall Health Chapter 8 Test
- Definition of mean median and mode in mathematics
- Atlante di anatomia umanapdf
- The Complete Film Dictionary
- Angell Summers Megapack
- James wesley rawles new book
- Dellabitare Corpi spazi oggetti immaginiepub
- Hma Pro Vpn
- De La Cocina Ala Mesa En 10 Minutos Castellano Pdf
- Pediatric Drug Development Concepts And Applications
- Minecraft Crazy Craft
- Professional Java EE Design Patterns PDFStormRG
- Univerzita Sv Cyrila A Metoda V Trnave 218vod Fakulta